연구동향
코로나바이러스(Covid-19) 치료제로 개발중인 약제 소개
작성자
관리자
작성일
2020-02-26 18:05
조회
7849
<코로나바이러스(Covid-19) 치료제로 개발중인 small-molecule drugs 소개>
중국에서 시작하여 전세계적으로 창궐하고 있는 Covid-19 바이러스는 RNA-바이러스로 현재 승인된 치료제가 없음.
Covid-19 바이러스 확산의 시급성 때문에 현재 다른 바이러스 치표제로 승인된 또는 개발중인 antiviral agents (HIV, HBV, HCV, influenza, SARS, MERS etc.) 를 drug repurposing 방법으로 Covid-19 바이러스를 억제하는 약제를 개발 하는 연구가 진행되고 있음.
<drug repurposing 으로 Covid-19 바이러스 억제 임상시험 중인 대표적 4가지 약제>
* Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
바로가기: Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2020, Feb. 10
* Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro
바로가기: Cell Res (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
*Learning from the Past: Possible Urgent Prevention and Treatment Options for Severe Acute Respiratory Infections Caused by 2019‐nCoV
바로가기: ChemBioChem, 2020
<Potential drug targets for beta-coronaviruses. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2020, Feb. 10>
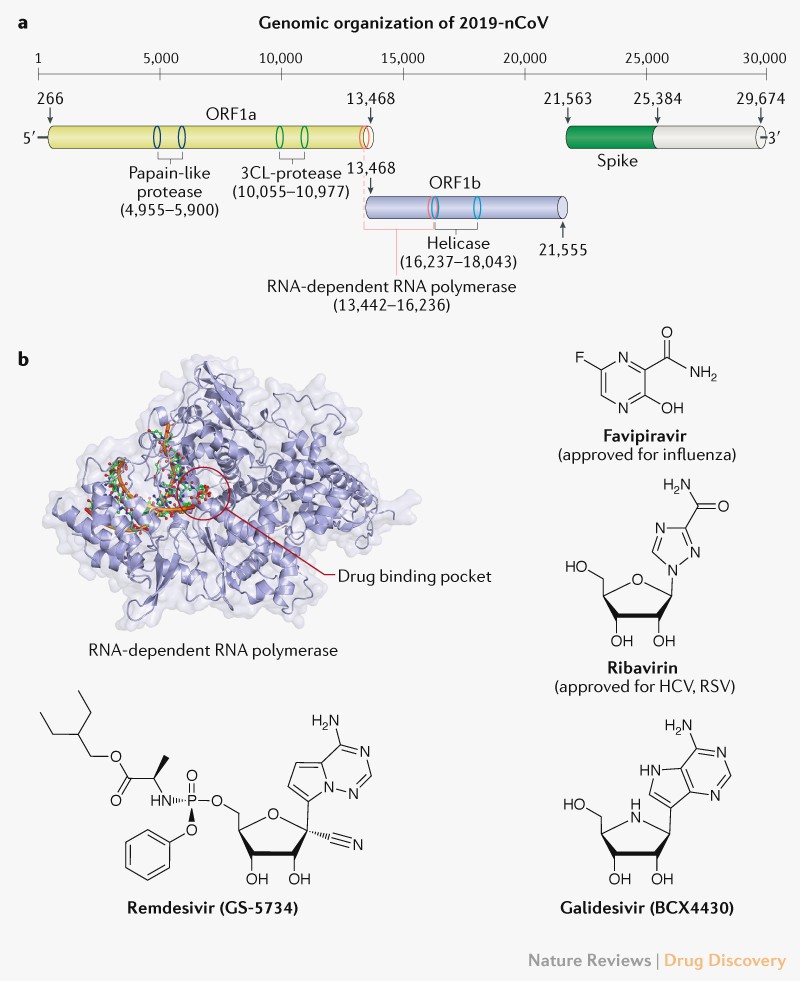
Fig. 1 | Potential drug targets for beta-coronaviruses. a | Genomic organization of 2019-nCoV (GenBank reference ID: MN908947.3), indicating the coding regions for proteins that are potential drug targets. b | A drug binding pocket is highlighted in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS (PDB: 6NUR, 3H5Y), visualized using PyMOL V1.7 (https://pymol.org). Chemical structures of four potential inhibitors interfering with the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of 2019-nCoV are also shown. 3CL, 3-chymotrypsin-like; HCV, hepatitis C virus; ORF, open reading frame; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus. Protein movies are available at www.virusface.com.
중국에서 시작하여 전세계적으로 창궐하고 있는 Covid-19 바이러스는 RNA-바이러스로 현재 승인된 치료제가 없음.
Covid-19 바이러스 확산의 시급성 때문에 현재 다른 바이러스 치표제로 승인된 또는 개발중인 antiviral agents (HIV, HBV, HCV, influenza, SARS, MERS etc.) 를 drug repurposing 방법으로 Covid-19 바이러스를 억제하는 약제를 개발 하는 연구가 진행되고 있음.
<drug repurposing 으로 Covid-19 바이러스 억제 임상시험 중인 대표적 4가지 약제>
- Favipiravir (approved for influenza; 한국화합물은행 보유)
- Ribavirin (approved for HCV, RSV; 한국화합물은행 보유)
- Remdesivir (GS-5734: 한국화합물은행 보유)
- Galidesivir (BCX4430)
* Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV)
바로가기: Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2020, Feb. 10
* Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro
바로가기: Cell Res (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
*Learning from the Past: Possible Urgent Prevention and Treatment Options for Severe Acute Respiratory Infections Caused by 2019‐nCoV
바로가기: ChemBioChem, 2020
<Potential drug targets for beta-coronaviruses. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2020, Feb. 10>

Fig. 1 | Potential drug targets for beta-coronaviruses. a | Genomic organization of 2019-nCoV (GenBank reference ID: MN908947.3), indicating the coding regions for proteins that are potential drug targets. b | A drug binding pocket is highlighted in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS (PDB: 6NUR, 3H5Y), visualized using PyMOL V1.7 (https://pymol.org). Chemical structures of four potential inhibitors interfering with the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of 2019-nCoV are also shown. 3CL, 3-chymotrypsin-like; HCV, hepatitis C virus; ORF, open reading frame; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus. Protein movies are available at www.virusface.com.